|
For
creating a new VM either you use an existing virtual disk,
either you create a new one.
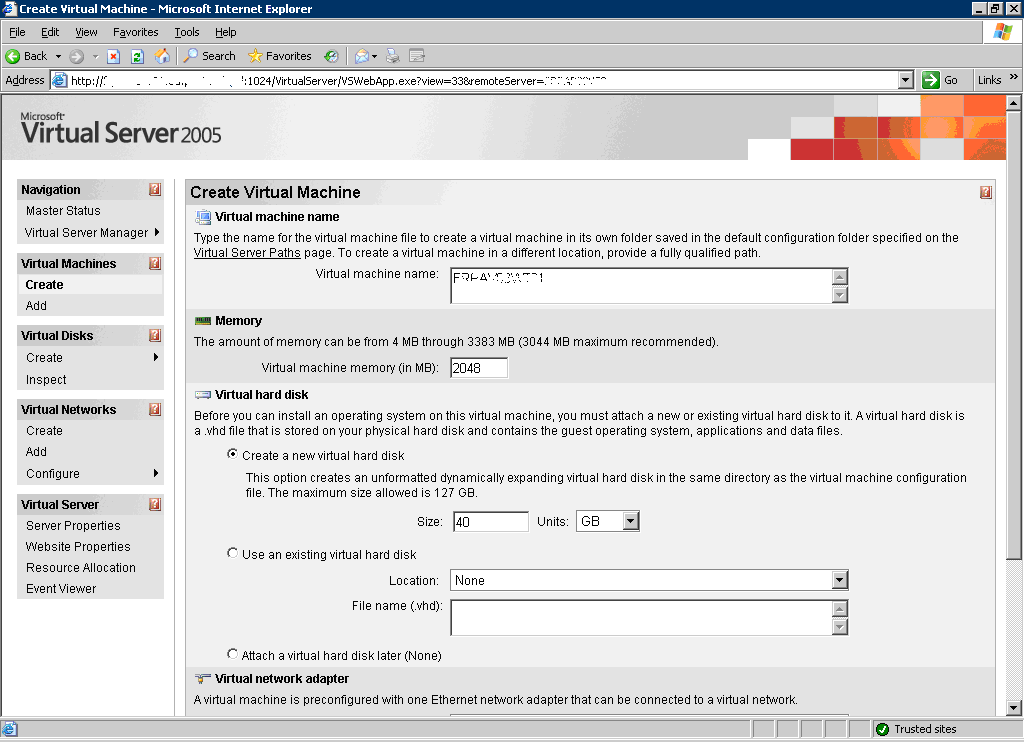
For creating a
new one from scratch :
Click on menu called Virtual Machines / Create
, then define :
_ Virtual Machine
Name : name given to VM
_ quantity of memory
for the VM
_ disk to use, in
the example, we create a dynamic disk : the file will grow while
files will be created on it, see next part for other types of
disks (here).

_
Network card to be used : either one real card which will be
virtualized, either a virtual network card (so you can test
without any risks on your network).
By clicking
on Next the new Virtual Machine is created with for example
following parameters :
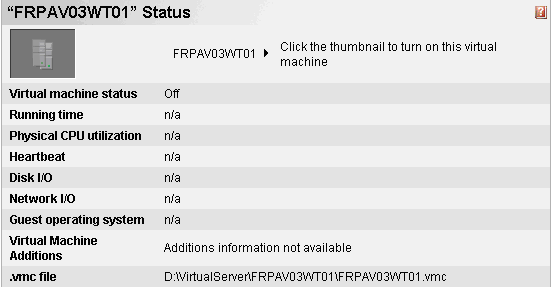
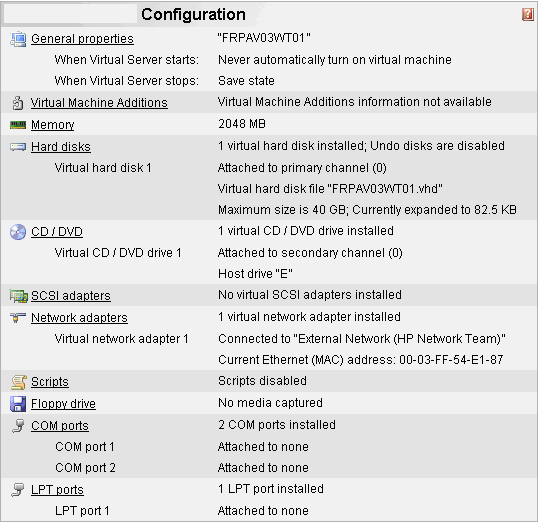
If you
double click on the graphical zone representing the screen (or
from the admin screen) the machine boots like a real PC (with an
AMI BIOS emulated) , if you created it from a new disk you will
now have to setup the new OS (the first CD ROM drive from the
host is virtualized, so if you place a bootable CD on it will be
loaded).
After
installation of the OS, you have to setup Virtual Virtual
Machine addition on the guest OS in order to integrate it
perfectly to Virtual Server :
In the menu Virtual Machines / Configure,
choose your VM (which must be started) :
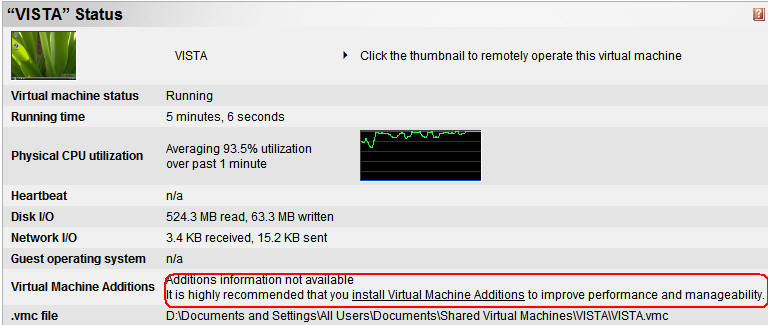
Click on Install Virtual Machine Additions
:
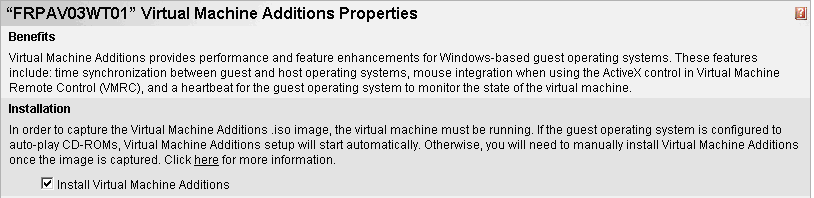
A new drive
is created automatically on the guest OS and setup is started :
(you will
have to restart the virtual machine)
-
Virtual machine optimization :
|
If your priority is
performance of the guest OS you can :
_ create different
non dynamics disks (fixed Size virtual disk)
_ store them on
different physical disks (RAID 1)
_ attach theses disks
to the virtual SCSI adapter
_ add network cards
on the server and then attach one physical card per
virtual device |
 |
|
Virtual Server supports four types of VHDs:
dynamically expanding, fixed-size, differencing, and
linked.
The host OS sees dynamically expanding and fixed-size
VHDs as a large .vhd file that contains the file system
for the guest VM.
_ Dynamically expanding disks start small and
automatically grow as the guest VM requires additional
storage. Much like a physical hard drive, a dynamically
expanding disk can grow only until it reaches its
predefined limit. As you'd expect, the guest VM
experiences a delay when the VHD must be expanded.
_ Fixed-size VHDs are allocated when you create them and
don't grow.
Dynamically expanding, fixed-size, and differencing VHDs
support using an optional undo disk. Undo disks let you
reset all changes that have been made to a dynamic,
fixed-size, or differencing disk.
Undo disks store all configuration and data changes made
to the VM during the session and prompt you to save or
discard the changes when you shut down the VM.
Differencing disks let you isolate changes that occur
within a guest VHD; all changes that occur in the parent
VHD are stored in the differencing disk.
Unlike an undo disk, which is associated with the entire
VM, a differencing disk is associated with a particular
VHD.
_ Linked Virtual Hard disk : allow you to link a real
physical disk or partition in order to convert it (must
not be used for production). |
 |
source :
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/virtualserver/2005/proddocs/vs_deploy_setup_VM_disks_hd.mspx?mfr=true
- Emulated
hardware within Virtual Server 2005 R2
:
BIOS
American Megatrends Inc. (AMI) basic input/output system (BIOS)
using the Intel 440BX with the PIIX4 chipset and the following
on-board components:
• Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS)
• Real-time clock
• Random access memory (RAM) and video RAM (VRAM)
• Memory controller
• Direct memory access (DMA) controller
• Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus
• ISA bus
• System Management (SM) bus
• Power management
• 8259 programmable interrupt controller (PIC)
• Programmable interrupt timer (PIT)
Floppy disk drives
floppy disk drive support for floppy disk drives of up to 1.44
megabytes (MB). Virtual Server 2005 also supports mapping to
real floppy disk drives or to floppy drive images.
Serial ports (COM ports)
Virtual Server 2005 emulates two serial ports. These ports can
be mapped to the host computer's serial ports.
Note You can only map to the standard COM 1 to COM 4 physical
serial ports. Additionally, you can do this only if the ports
are using standard I/O address ranges. Therefore, many add-on
serial cards do not work with Virtual Server. However, older ISA
cards that contain jumper switches may work.
Printer port (LPT port)
Virtual Server 2005 emulates a single printer port that maps to
the host computer's parallel port.
Note You can only map to the LPT1
physical parallel port. Additionally, you can do this only if
the port is using the standard I/O address range of 378h to
37Fh. Therefore, add-on parallel cards are not supported in
Virtual Server 2005.
Mouse :
Standard PS/2 Microsoft IntelliMouse device that can be mapped
to either a PS/2 mouse or to a USB mouse on the host computer.
Keyboard
Virtual Server 2005 emulates a standard PS/2 101-key Microsoft
keyboard that can be mapped to either a PS/2 keyboard or to a
USB keyboard on the host computer.
Ethernet controller
Virtual Server 2005 emulates a multi-port Digital Equipment
Corporation (DEC) 21140 10/100TX 100 megabit Ethernet network
adapter with one to four network connections, multiplexed on a
single Virtual Server slot. An unlimited number of virtual
networks are supported. All supported versions of the Windows
operating system include drivers for the DEC 21140 network card.
Note The DEC 21140 network card may appear on the virtual
machine as "Intel 21140." These are equivalent network adapters.
Processor
A virtual computer uses the CPU of the physical computer.
Therefore a virtual machine has the same type of CPU as the
physical computer where Virtual Server 2005 is installed.
Although Virtual Server runs on systems that have up to 32
processors, guest operating systems only see a single CPU for
each virtual machine. Virtual Server is optimized for industry
standard hardware that has up to eight CPUs.
Memory
Virtual Server 2005 supports up to 64 gigabytes (GB) of RAM on
the host computer and up to 3.6 GB for each virtual machine.
Highly scalable systems can only support very large memory
configurations if PAE (Physical Addressing Extensions) and AWE
(Advanced Windowing Extensions) are installed on the host
operating system.
Video card
Virtual Server 2005 emulates the S3 Trio64 graphics adapter with
4 MB of VRAM, Visual Electronics Standards Association (VESA)
2.0 compliant VGA and SVGA support, and support for DirectX.
Note Before a virtual machine can recognize every available
resolution, you must install the virtual machine additions.
Integrated device electronics (IDE)/ATAPI storage
Virtual Server 2005 emulates up to 4 IDE devices, such as hard
drives, CD drives, DVD-ROM drives, or ISO images. Additionally,
Virtual Server 2005 emulates virtual disk images of up to 128 GB
per IDE channel.
Note IDE is limited to one transaction per
bus, whether it is a physical IDE device or a virtual IDE device.
If you have two IDE disks attached to the same virtual or
physical IDE bus, you are limited to a single transaction for
both devices.
Small computer system interface (SCSI) storage
Virtual Server 2005 emulates the Adaptec 7870 SCSI controller
chip set. This chip set has up to four virtual SCSI adapters.
Each SCSI hard disk can be up to two terabytes. Each virtual
SCSI adapter can support up to seven virtual SCSI hard drives.
Therefore, the total direct-connect storage capacity is over 56
terabytes per virtual machine. Virtual Server supports simple
active or passive clustering between virtual machines.
Note SCSI controllers and disks support multiple, concurrent
input/output (I/O) to increase the performance of both physical
SCSI devices and virtual SCSI devices. We recommend that you use
SCSI whenever you can.
Sound card
Virtual Server 2005 does not include an emulated sound card.
|











